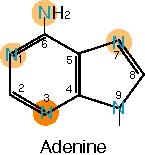
1. Draw a diagram of the DNA base, adenine. Show the positions of any keto, hydroxyl or amino groups. You may number the ring system if you wish, but it is not necessary. (5 points)

2. On the diagram you have just drawn, circle the positions that can be methylated by S-adenosyl methionine. Which position is most readily methylated? (2 points)
The methylatable positions are indicated in the above diagram by shaded circles. Darker shading indicates the preferred methylation site (position 3). Note that in this base, which lacks oxygens, all nitrogens except the nitrogen at position 9 (which is already saturated by N-C bonds) can be methylated. When studying for this exam, you could have helped yourself by noticing that, for all 4 bases, ALL nitrogens and oxygens (except the saturated ones at position 9 of purines or position 1 of pyrimidines) can be methylated, and NO CARBON atoms can be methylated.
3. Which of the following pathways is responsible for correcting adenine methylation: (a) photolyase; (b) mismatch repair; (c)base excision repair; (d) nucleotide excision repair; (e) transcription-coupled repair, (f) non-homologous end joining? (2 points)
Base excision repair is the pathway that removes damaged bases, including methylated bases.
Click here to return to list of questions from previous exams.